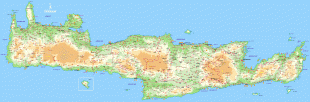
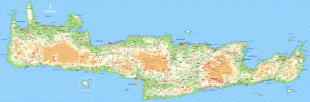
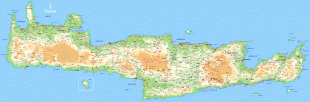
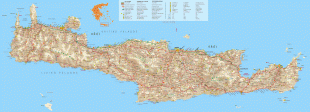
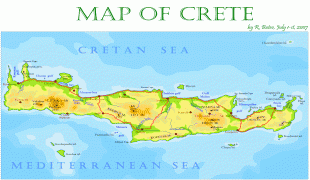
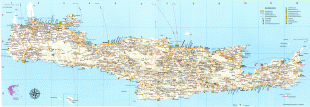
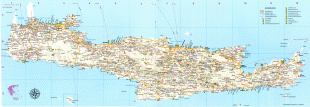
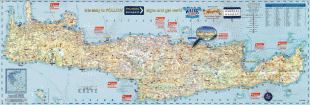
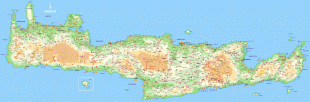
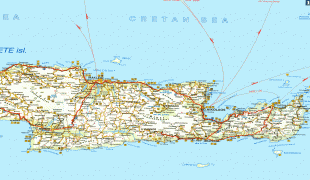
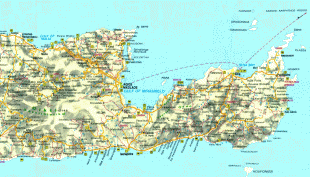
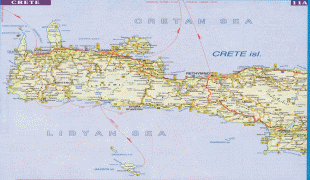
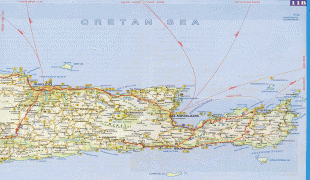
Crete
Crete and a number of islands and islets that surround it constitute the Region of Crete (Περιφέρεια Κρήτης), which is the southernmost of the 13 top-level administrative units of Greece, and the fifth most populous of Greece's regions. Its capital and largest city is Heraklion, on the north shore of the island. , the region had a population of 636,504. The Dodecanese are located to the northeast of Crete, while the Cyclades are situated to the north, separated by the Sea of Crete. The Peloponnese is to the region's northwest.
Humans have inhabited the island since at least 130,000 years ago, during the Paleolithic age. Crete was the centre of Europe's first advanced civilization, the Minoans, from 2700 to 1420 BC. The Minoan civilization was overrun by the Mycenaean civilization from mainland Greece. Crete was later ruled by Rome, then successively by the Byzantine Empire, Andalusian Arabs, the Venetian Republic, and the Ottoman Empire. In 1898 Crete, whose people had for some time wanted to join the Greek state, achieved independence from the Ottomans, formally becoming the Cretan State. Crete became part of Greece in December 1913.
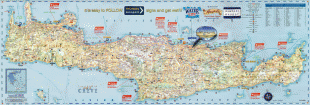
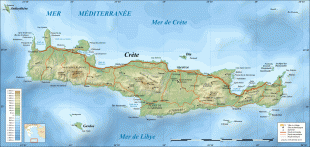
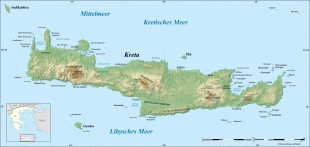
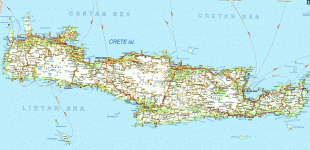
The island is mostly mountainous, and its character is defined by a high mountain range crossing from west to east. It includes Crete's highest point, Mount Ida, and the range of the White Mountains (Lefka Ori) with 30 summits above 2000 m in altitude and the Samaria Gorge, a World Biosphere Reserve. Crete forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece, while retaining its own local cultural traits (such as its own poetry and music). The Nikos Kazantzakis airport at Heraklion and the Daskalogiannis airport at Chania serve international travelers. The palace of Knossos, a Bronze Age settlement and ancient Minoan city, is also located in Heraklion.
The earliest references to the island of Crete come from texts from the Syrian city of Mari dating from the 18th century BC, where the island is referred to as Kaptara. This is repeated later in Neo-Assyrian records and the Bible (Caphtor). It was known in ancient Egyptian as Keftiu or kftı͗w, strongly suggesting a similar Minoan name for the island.
The current name Crete is first attested in the 15th century BC in Mycenaean Greek texts, written in Linear B, through the words ke-re-te (, *Krētes; later Greek: Κρῆτες, plural of Κρής ) and ke-re-si-jo (, *Krēsijos; later Greek: Κρήσιος , 'Cretan'). In Ancient Greek, the name Crete (Κρήτη) first appears in Homer's Odyssey. Its etymology is unknown. One proposal derives it from a hypothetical Luwian word *kursatta (compare kursawar 'island', kursattar 'cutting, sliver'). Another proposal suggests that it derives from the ancient Greek word "κραταιή" (krataie̅), meaning strong or powerful, the reasoning being that Crete was the strongest thalassocracy during ancient times.
In Latin, the name of the island became Creta. The original Arabic name of Crete was Iqrīṭiš (اقريطش < (τῆς) Κρήτης), but after the Emirate of Crete's establishment of its new capital at ربض الخندق Rabḍ al-Ḫandaq (modern Heraklion; Ηράκλειο, Irákleio), both the city and the island became known as Χάνδαξ (Chandax) or Χάνδακας (Chandakas), which gave Latin, Italian, and Venetian Candia, from which were derived French Candie and English Candy or Candia. Under Ottoman rule, in Ottoman Turkish, Crete was called Girit (كريد). In the Hebrew Bible, Crete is referred to as (כְּרֵתִים) "kretim".
Map - Crete
Map
Country - Greece
 |
 |
| Flag of Greece | |
Greece is considered the cradle of Western civilization, being the birthplace of democracy, Western philosophy, Western literature, historiography, political science, major scientific and mathematical principles, theatre and the Olympic Games. From the eighth century BC, the Greeks were organised into various independent city-states, known as poleis (singular polis), which spanned the Mediterranean and the Black Sea. Philip II of Macedon united most of present-day Greece in the fourth century BC, with his son Alexander the Great rapidly conquering much of the ancient world, from the eastern Mediterranean to the North Western parts of India. The subsequent Hellenistic period saw the height of Greek culture and influence in antiquity. Greece was annexed by Rome in the second century BC, becoming an integral part of the Roman Empire and its continuation, the Byzantine Empire, which was culturally and linguistically predominantly Greek.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUR | Euro | € | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| EN | English language |
| FR | French language |
| EL | Greek language |