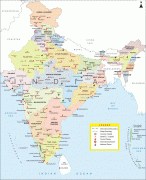
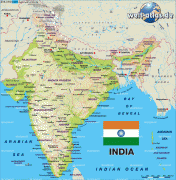
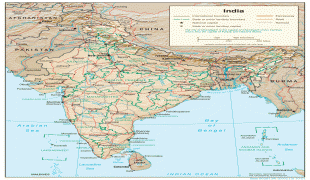
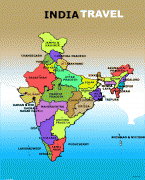
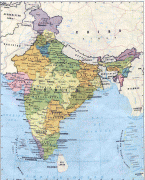
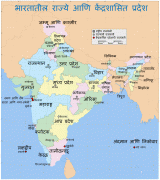
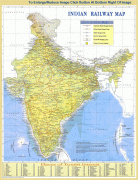
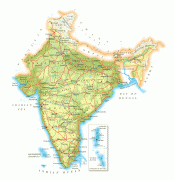
India (Republic of India)
 |
 |
| Flag of India | |
Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago. Their long occupation, initially in varying forms of isolation as hunter-gatherers, has made the region highly diverse, second only to Africa in human genetic diversity. Settled life emerged on the subcontinent in the western margins of the Indus river basin 9,000 years ago, evolving gradually into the Indus Valley Civilisation of the third millennium BCE. By, an archaic form of Sanskrit, an Indo-European language, had diffused into India from the northwest. (a) (b) (c), "In Punjab, a dry region with grasslands watered by five rivers (hence ‘panch’ and ‘ab’) draining the western Himalayas, one prehistoric culture left no material remains, but some of its ritual texts were preserved orally over the millennia. The culture is called Aryan, and evidence in its texts indicates that it spread slowly south-east, following the course of the Yamuna and Ganga Rivers. Its elite called itself Arya (pure) and distinguished themselves sharply from others. Aryans led kin groups organized as nomadic horse-herding tribes. Their ritual texts are called Vedas, composed in Sanskrit. Vedic Sanskrit is recorded only in hymns that were part of Vedic rituals to Aryan gods. To be Aryan apparently meant to belong to the elite among pastoral tribes. Texts that record Aryan culture are not precisely datable, but they seem to begin around 1200 BCE with four collections of Vedic hymns (Rg, Sama, Yajur, and Artharva)."
(d), "Although the collapse of the Indus valley civilization is no longer believed to have been due to an ‘Aryan invasion’ it is widely thought that, at roughly the same time, or perhaps a few centuries later, new Indo-Aryan-speaking people and influences began to enter the subcontinent from the north-west. Detailed evidence is lacking. Nevertheless, a predecessor of the language that would eventually be called Sanskrit was probably introduced into the north-west sometime between 3,900 and 3,000 years ago. This language was related to one then spoken in eastern Iran; and both of these languages belonged to the Indo-European language family. ... It seems likely that various small-scale migrations were involved in the gradual introduction of the predecessor language and associated cultural characteristics. However, there may not have been a tight relationship between movements of people on the one hand, and changes in language and culture on the other. Moreover, the process whereby a dynamic new force gradually arose—a people with a distinct ideology who eventually seem to have referred to themselves as ‘Arya’—was certainly two-way. That is, it involved a blending of new features which came from outside with other features—probably including some surviving Harappan influences—that were already present. Anyhow, it would be quite a few centuries before Sanskrit was written down. And the hymns and stories of the Arya people—especially the Vedas and the later Mahabharata and Ramayana epics—are poor guides as to historical events. Of course, the emerging Arya were to have a huge impact on the history of the subcontinent. Nevertheless, little is known about their early presence."; (e), "The expansion of Aryan culture is supposed to have begun around 1500 BCE. It should not be thought that this Aryan emergence (though it implies some migration) necessarily meant either a sudden invasion of new peoples, or a complete break with earlier traditions. It comprises a set of cultural ideas and practices, upheld by a Sanskrit-speaking elite, or Aryans. The features of this society are recorded in the Vedas." Its evidence today is found in the hymns of the Rigveda. Preserved by a resolutely vigilant oral tradition, the Rigveda records the dawning of Hinduism in India.(a) ; (b) ; (c) (d) The Dravidian languages of India were supplanted in the northern and western regions. By, stratification and exclusion by caste had emerged within Hinduism, and Buddhism and Jainism had arisen, proclaiming social orders unlinked to heredity. Early political consolidations gave rise to the loose-knit Maurya and Gupta Empires based in the Ganges Basin. Their collective era was suffused with wide-ranging creativity, but also marked by the declining status of women, and the incorporation of untouchability into an organised system of belief. In South India, the Middle kingdoms exported Dravidian-languages scripts and religious cultures to the kingdoms of Southeast Asia.
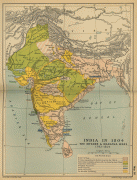
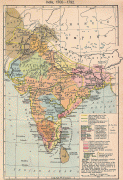
In the early medieval era, Christianity, Islam, Judaism, and Zoroastrianism became established on India's southern and western coasts. Muslim armies from Central Asia intermittently overran India's northern plains, eventually founding the Delhi Sultanate, and drawing northern India into the cosmopolitan networks of medieval Islam. In the 15th century, the Vijayanagara Empire created a long-lasting composite Hindu culture in south India. In the Punjab, Sikhism emerged, rejecting institutionalised religion. The Mughal Empire, in 1526, ushered in two centuries of relative peace, leaving a legacy of luminous architecture. Gradually expanding rule of the British East India Company followed, turning India into a colonial economy, but also consolidating its sovereignty. British Crown rule began in 1858. The rights promised to Indians were granted slowly, but technological changes were introduced, and modern ideas of education and the public life took root. A pioneering and influential nationalist movement emerged, which was noted for nonviolent resistance and became the major factor in ending British rule. In 1947 the British Indian Empire was partitioned into two independent dominions, a Hindu-majority Dominion of India and a Muslim-majority Dominion of Pakistan, amid large-scale loss of life and an unprecedented migration.
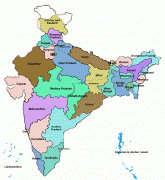
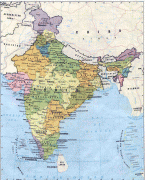
India has been a federal republic since 1950, governed through a democratic parliamentary system. It is a pluralistic, multilingual and multi-ethnic society. India's population grew from 361 million in 1951 to 1.4 billion in 2022. During the same time, its nominal per capita income increased from US$64 annually to US$1,498, and its literacy rate from 16.6% to 74%. From being a comparatively destitute country in 1951, India has become a fast-growing major economy and a hub for information technology services, with an expanding middle class. It has a space programme which includes several planned or completed extraterrestrial missions. Indian movies, music, and spiritual teachings play an increasing role in global culture. India has substantially reduced its rate of poverty, though at the cost of increasing economic inequality. India is a nuclear-weapon state, which ranks high in military expenditure. It has disputes over Kashmir with its neighbours, Pakistan and China, unresolved since the mid-20th century. Among the socio-economic challenges India faces are gender inequality, child malnutrition, and rising levels of air pollution. India's land is megadiverse, with four biodiversity hotspots. Its forest cover comprises 21.7% of its area. India's wildlife, which has traditionally been viewed with tolerance in India's culture, is supported among these forests, and elsewhere, in protected habitats.
According to the Oxford English Dictionary (third edition 2009), the name "India" is derived from the Classical Latin India, a reference to South Asia and an uncertain region to its east; and in turn derived successively from: Hellenistic Greek India ( Ἰνδία); ancient Greek Indos ( Ἰνδός); Old Persian Hindush, an eastern province of the Achaemenid Empire; and ultimately its cognate, the Sanskrit Sindhu, or "river," specifically the Indus River and, by implication, its well-settled southern basin. The ancient Greeks referred to the Indians as Indoi , which translates as "The people of the Indus".
The term Bharat, mentioned in both Indian epic poetry and the Constitution of India, is used in its variations by many Indian languages. A modern rendering of the historical name Bharatavarsha, which applied originally to North India, Bharat gained increased currency from the mid-19th century as a native name for India.
Hindustan is a Middle Persian name for India, introduced during the Mughal Empire and used widely since. Its meaning has varied, referring to a region encompassing present-day northern India and Pakistan or to India in its near entirety.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| INR | Indian rupee | ₹ | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| AS | Assamese language |
| BN | Bengali language |
| BH | Bihari languages |
| EN | English language |
| GU | Gujarati language |
| HI | Hindi |
| KN | Kannada language |
| ML | Malayalam language |
| MR | Marathi language |
| OR | Oriya language |
| PA | Panjabi language |
| TA | Tamil language |
| TE | Telugu language |
| UR | Urdu |