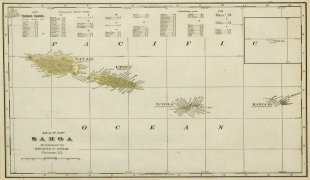
Samoan Islands (Independent State of Samoa)
 |
 |
| Flag of Samoa | |
The population of the Samoan Islands is approximately 250,000. The inhabitants have in common the Samoan language, a culture known as fa'a Samoa, and an indigenous form of governance called fa'amatai. Samoans are one of the largest Polynesian populations in the world, and most are of exclusively Samoan ancestry.
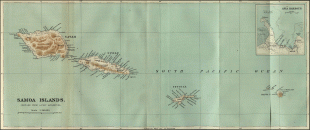
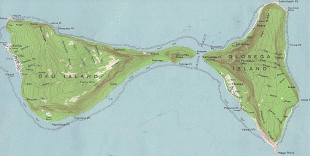
The oldest known evidence of human activity in the Samoan Islands dates to around 1050 BCE. It comes from a Lapita site at Mulifanua wharf on Upolu island. In 1768, the eastern islands were visited by the French explorer Bougainville, who named them the Navigator Islands. That name was used by missionaries until about 1845, and in official European dispatches until about 1870.
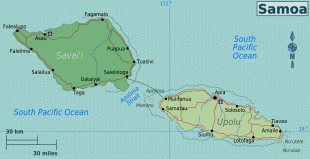
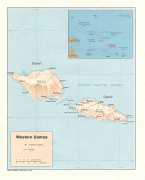
Politically, the Samoan Islands are divided into two jurisdictions:
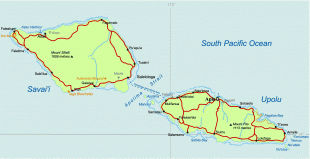
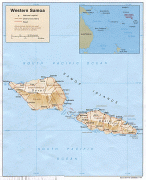
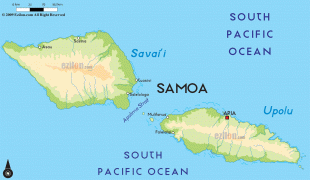
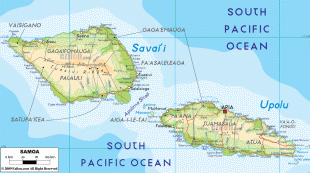
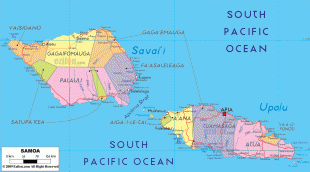
* ?? samoa, an independent nation that gained political independence from New Zealand in 1962. It comprises the western half of the Samoa islands, (2831 km2 and 196,000 inhabitants (2016)). It was known as German Samoa from 1900 to 1914, and as Western Samoa until 1997.
* Capital: Apia; currency: Samoan tala.
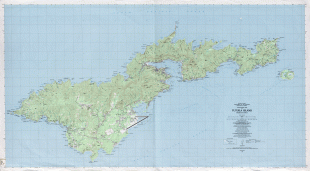
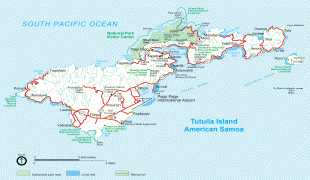
* ?? american samoa, an unincorporated territory of the United States comprising the eastern half of the Samoa Islands. (199 km2 and 49,710 inhabitants (2020)).
* Capital: Pago Pago; currency: US dollar.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| WST | Samoan tala | T | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| EN | English language |
| SM | Samoan language |