Baghdad
Baghdad (بَغْدَاد, بەغدا) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. In 762 CE, Baghdad was chosen as the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate, and became its most notable major development project. Within a short time, the city evolved into a significant cultural, commercial, and intellectual center of the Muslim world. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the "Center of Learning".
Baghdad was the largest city in the world for much of the Abbasid era during the Islamic Golden Age, peaking at a population of more than a million. The city was largely destroyed at the hands of the Mongol Empire in 1258, resulting in a decline that would linger through many centuries due to frequent plagues and multiple successive empires. With the recognition of Iraq as an independent state (formerly the British Mandate of Mesopotamia) in 1932, Baghdad gradually regained some of its former prominence as a significant center of Arab culture, with a population variously estimated at 6 or over 7 million. Compared to its large population, it has a small area at just 673 square kilometers (260 sq mi).
The city has faced severe infrastructural damage due to the Iraq War, which began with the United States-led invasion of Iraq in 2003 and lasted until 2011, and the subsequent insurgency and renewed war that lasted until 2017, resulting in a substantial loss of cultural heritage and historical artifacts. During this period, Baghdad had one of the highest rates of terrorist attacks in the world. However, terrorist attacks are rare and have been declining since the territorial defeat of the Islamic State militant group in Iraq in 2017.
The name Baghdad is pre-Islamic, and its origin is disputed. The site where the city of Baghdad developed has been populated for millennia. By the eighth century, several villages had developed there, including a Sasanian hamlet called Baghdad, the name which would come to be used for the Abbasid metropolis.
Arab authors, realizing the pre-Islamic origins of Baghdad's name, generally looked for its roots in Middle Persian. They suggested various meanings, the most common of which was "bestowed by God". Modern scholars generally tend to favor this etymology, which views the word as a Persian compound of bagh "god" and dād "given". In Old Persian the first element can be traced to boghu and is related to Indo-Iranian bhag and Slavic bog "god." A similar term in Middle Persian is the name Mithradāt (Mehrdad in New Persian), known in English by its borrowed Hellenistic form Mithridates, meaning "Given by Mithra" (dāt is the more archaic form of dād, related to Sanskrit dāt, Latin dat and English donor ), ultimately borrowed from Persian Mehrdad. There are a number of other locations whose names are compounds of the Middle Persian word bagh, including Baghlan and Bagram in Afghanistan, Baghshan in Iran itself, and Baghdati in Georgia, which likely share the same etymological Iranic origins.
A few authors have suggested older origins for the name, in particular the name Bagdadu or Hudadu that existed in Old Babylonian (spelled with a sign that can represent both bag and hu), and the Jewish Babylonian Aramaic name of a place called "Baghdatha" (בגדתא. Some scholars suggested Aramaic derivations.
Christophe Wall-Romana has suggested that name of "Baghdad" is derived from none other than "Akkad" because the cuneiform logogram for Akkad (????) is actually pronounced "a-ga-dèKI" ("Agade") and its resemblance to "Baghdad" is compelling.
When the Abbasid caliph al-Mansur founded a completely new city for his capital, he chose the name City of Peace, which now refers to the Round city of Baghdad proper. This was the official name on coins, weights, and other official usage, although the common people continued to use the old name. By the 11th century, "Baghdad" became almost the exclusive name for the world-renowned metropolis.
Christophe Wall-Romana has suggested that al-Mansur's choice to found his 'new city' at Baghdad because of its strategic location was the same criteria which influenced Sargon's choice to found the original city of Akkad in the exact same location.
Baghdad was the largest city in the world for much of the Abbasid era during the Islamic Golden Age, peaking at a population of more than a million. The city was largely destroyed at the hands of the Mongol Empire in 1258, resulting in a decline that would linger through many centuries due to frequent plagues and multiple successive empires. With the recognition of Iraq as an independent state (formerly the British Mandate of Mesopotamia) in 1932, Baghdad gradually regained some of its former prominence as a significant center of Arab culture, with a population variously estimated at 6 or over 7 million. Compared to its large population, it has a small area at just 673 square kilometers (260 sq mi).
The city has faced severe infrastructural damage due to the Iraq War, which began with the United States-led invasion of Iraq in 2003 and lasted until 2011, and the subsequent insurgency and renewed war that lasted until 2017, resulting in a substantial loss of cultural heritage and historical artifacts. During this period, Baghdad had one of the highest rates of terrorist attacks in the world. However, terrorist attacks are rare and have been declining since the territorial defeat of the Islamic State militant group in Iraq in 2017.
The name Baghdad is pre-Islamic, and its origin is disputed. The site where the city of Baghdad developed has been populated for millennia. By the eighth century, several villages had developed there, including a Sasanian hamlet called Baghdad, the name which would come to be used for the Abbasid metropolis.
Arab authors, realizing the pre-Islamic origins of Baghdad's name, generally looked for its roots in Middle Persian. They suggested various meanings, the most common of which was "bestowed by God". Modern scholars generally tend to favor this etymology, which views the word as a Persian compound of bagh "god" and dād "given". In Old Persian the first element can be traced to boghu and is related to Indo-Iranian bhag and Slavic bog "god." A similar term in Middle Persian is the name Mithradāt (Mehrdad in New Persian), known in English by its borrowed Hellenistic form Mithridates, meaning "Given by Mithra" (dāt is the more archaic form of dād, related to Sanskrit dāt, Latin dat and English donor ), ultimately borrowed from Persian Mehrdad. There are a number of other locations whose names are compounds of the Middle Persian word bagh, including Baghlan and Bagram in Afghanistan, Baghshan in Iran itself, and Baghdati in Georgia, which likely share the same etymological Iranic origins.
A few authors have suggested older origins for the name, in particular the name Bagdadu or Hudadu that existed in Old Babylonian (spelled with a sign that can represent both bag and hu), and the Jewish Babylonian Aramaic name of a place called "Baghdatha" (בגדתא. Some scholars suggested Aramaic derivations.
Christophe Wall-Romana has suggested that name of "Baghdad" is derived from none other than "Akkad" because the cuneiform logogram for Akkad (????) is actually pronounced "a-ga-dèKI" ("Agade") and its resemblance to "Baghdad" is compelling.
When the Abbasid caliph al-Mansur founded a completely new city for his capital, he chose the name City of Peace, which now refers to the Round city of Baghdad proper. This was the official name on coins, weights, and other official usage, although the common people continued to use the old name. By the 11th century, "Baghdad" became almost the exclusive name for the world-renowned metropolis.
Christophe Wall-Romana has suggested that al-Mansur's choice to found his 'new city' at Baghdad because of its strategic location was the same criteria which influenced Sargon's choice to found the original city of Akkad in the exact same location.
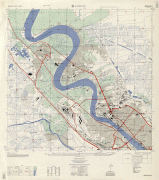
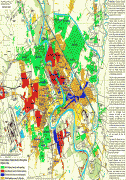
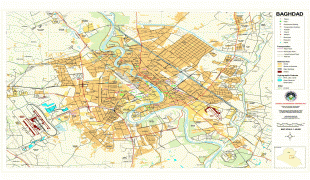
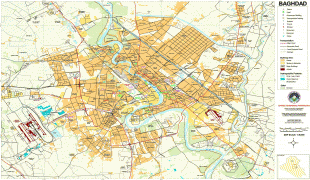
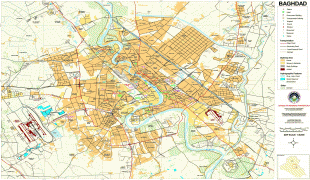
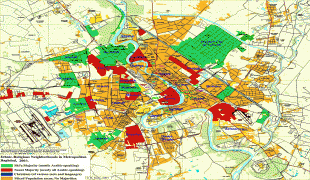
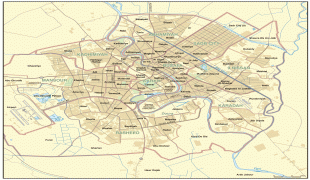
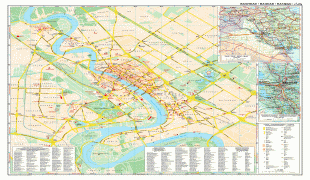
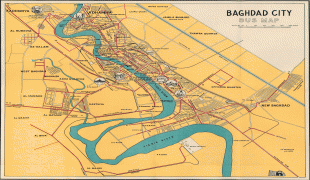
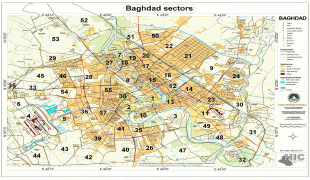
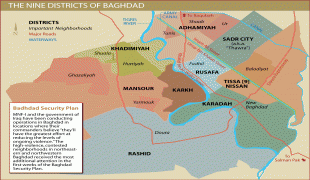
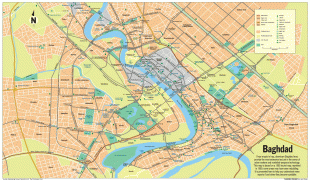
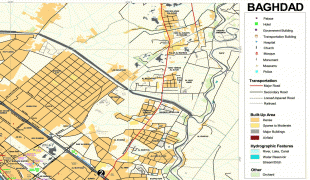
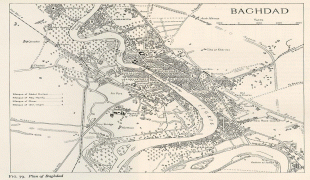
Map - Baghdad
Map
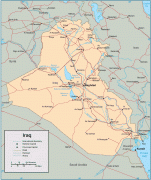
Country - Mesopotamia
 |
|
| Flag of Iraq | |
The Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrians and Babylonians) originating from different areas in present-day Iraq, dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of written history (c. 3100 BC) to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire. Later the Arameans dominated major parts of Mesopotamia (c. 900 BC – 270 AD).
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| IQD | Iraqi dinar | عد | 3 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| AR | Arabic language |
| HY | Armenian language |
| KU | Kurdish language |