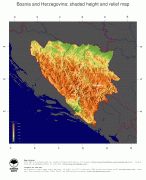
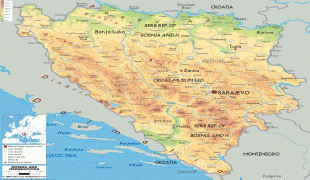
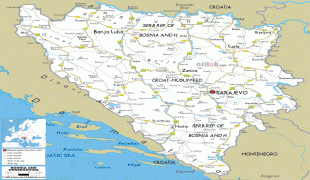
Bosnia and Herzegovina (Bosnia and Herzegovina)
 |
 |
| Flag of Bosnia and Herzegovina | |
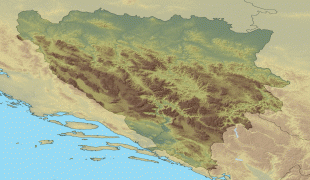
The area that is now Bosnia and Herzegovina has been inhabited by humans since at least the Upper Paleolithic, but evidence suggests that during the Neolithic age, permanent human settlements were established, including those that belonged to the Butmir, Kakanj, and Vučedol cultures. After the arrival of the first Indo-Europeans, the area was populated by several Illyrian and Celtic civilizations. Culturally, politically, and socially, the country has a rich and complex history. The ancestors of the South Slavic peoples that populate the area today arrived during the 6th through the 9th century. In the 12th century, the Banate of Bosnia was established; by the 14th century, this had evolved into the Kingdom of Bosnia. In the mid-15th century, it was annexed into the Ottoman Empire, under whose rule it remained until the late 19th century. The Ottomans brought Islam to the region, and altered much of the country's cultural and social outlook.
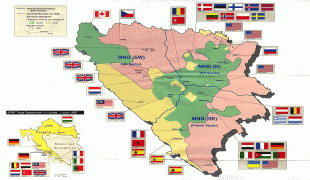
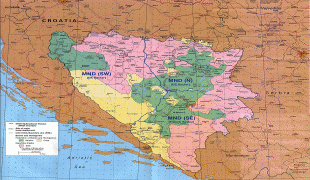
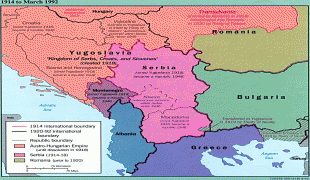
From the late 19th century until World War I, the country was annexed into the Austro-Hungarian monarchy. In the interwar period, Bosnia and Herzegovina was part of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. After World War II, it was granted full republic status in the newly formed Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. In 1992, following the breakup of Yugoslavia, the republic proclaimed independence. This was followed by the Bosnian War, which lasted until late 1995 and was brought to a close with the signing of the Dayton Agreement.
Today, the country is home to three main ethnic groups, designated "constituent peoples" in the country's constitution. The Bosniaks are the largest group of the three, the Serbs are the second-largest, and the Croats are the third-largest. In English, all natives of Bosnia and Herzegovina, regardless of ethnicity, are called Bosnian. Minorities, who under the constitution are categorized as "others", include Jews, Roma, Albanians, Montenegrins, Ukrainians and Turks.
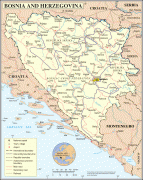
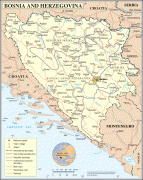
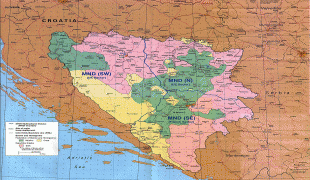
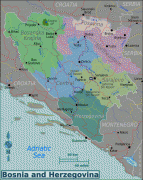
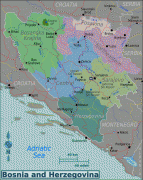
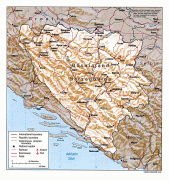
Bosnia and Herzegovina has a bicameral legislature and a three-member presidency made up of one member from each of the three major ethnic groups. However, the central government's power is highly limited, as the country is largely decentralized. It comprises two autonomous entities—the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Republika Srpska—and a third unit, the Brčko District, which is governed by its own local government. The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina furthermore consists of 10 cantons.
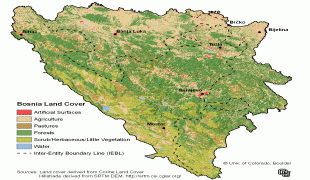
Bosnia and Herzegovina is a developing country and ranks 74th in the Human Development Index. Its economy is dominated by industry and agriculture, followed by tourism and the service sector. Tourism has increased significantly in recent years. The country has a social-security and universal-healthcare system, and primary and secondary level education is free. It is a member of the UN, the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, the Council of Europe, the Partnership for Peace, and the Central European Free Trade Agreement; it is also a founding member of the Union for the Mediterranean, established in July 2008. Bosnia and Herzegovina is an EU candidate country and has also been a candidate for NATO membership since April 2010, when it received a Membership Action Plan.
The first preserved widely acknowledged mention of a form of the name "Bosnia" is in De Administrando Imperio, a politico-geographical handbook written by the Byzantine emperor Constantine VII in the mid-10th century (between 948 and 952) describing the "small land" (χωρίον in Greek) of "Bosona" (Βοσώνα), where the Serbs dwell. Bosnia was also mentioned in the DAI (χωριον βοσονα, small land of Bosnia), as a region of Baptized Serbia.
The name of the land is believed to derive from the hydronym of the river Bosna that courses through the Bosnian heartland. The river's name Bosna most likely was itself derived from the toponym Basona (Hittite for forestland) or Basoa (Basque for forest). According to philologist Anton Mayer, the name Bosna could derive from Illyrian *"Bass-an-as", which in turn could derive from the Proto-Indo-European root bʰegʷ-, meaning "the running water". According to the English medievalist William Miller, the Slavic settlers in Bosnia "adapted the Latin designation ... Basante, to their own idiom by calling the stream Bosna and themselves Bosniaks".
The name Herzegovina means "herzog's [land]", and "herzog" derives from the German word for "duke". It originates from the title of a 15th-century Bosnian magnate, Stjepan Vukčić Kosača, who was "Herceg [Herzog] of Hum and the Coast" (1448). Hum (formerly called Zachlumia) was an early medieval principality that had been conquered by the Bosnian Banate in the first half of the 14th century. When the Ottomans took over administration of the region, they called it the Sanjak of Herzegovina (Hersek). It was included within the Bosnia Eyalet until the formation of the short-lived Herzegovina Eyalet in the 1830s, which reemerged in the 1850s, after which the administrative region became commonly known as Bosnia and Herzegovina.
On initial proclamation of independence in 1992, the country's official name was the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina, but following the 1995 Dayton Agreement and the new constitution that accompanied it, the official name was changed to Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| BAM | Bosnia and Herzegovina convertible mark | KM or КМ | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| BS | Bosnian language |
| HR | Croatian language |
| SR | Serbian language |