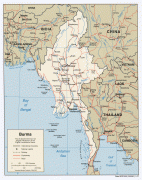
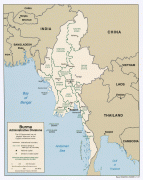
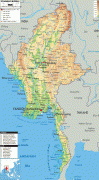
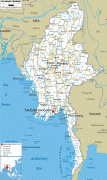
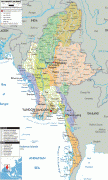
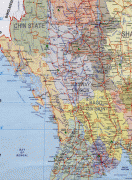
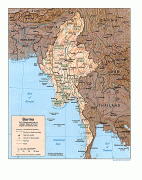
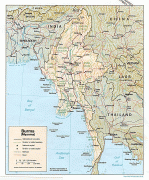
Burma (Union of Burma)
 |
 |
| Flag of Myanmar | |
Early civilisations in the area included the Tibeto-Burman-speaking Pyu city-states in Upper Myanmar and the Mon kingdoms in Lower Myanmar. In the 9th century, the Bamar people entered the upper Irrawaddy valley, and following the establishment of the Pagan Kingdom in the 1050s, the Burmese language, culture, and Theravada Buddhism slowly became dominant in the country. The Pagan Kingdom fell to Mongol invasions, and several warring states emerged. In the 16th century, reunified by the Taungoo dynasty, the country became the largest empire in the history of Southeast Asia for a short period.
The early 19th-century Konbaung dynasty ruled over an area that included modern Myanmar and briefly controlled Manipur and Assam as well. The British East India Company seized control of the administration of Myanmar after three Anglo-Burmese Wars in the 19th century, and the country became a British colony. After a brief Japanese occupation, Myanmar was reconquered by the Allies and gained independence in 1948. Following a coup d'état in 1962, it became a military dictatorship under the Burma Socialist Programme Party.
For most of its independent years, the country has been engulfed in rampant ethnic strife and its myriad ethnic groups have been involved in one of the world's longest-running ongoing civil wars. During this time, the United Nations and several other organisations have reported consistent and systemic human rights violations in the country. In 2011, the military junta was officially dissolved following a 2010 general election, and a nominally civilian government was installed. This, along with the release of Aung San Suu Kyi and political prisoners and successful elections in 2015, improved the country's human rights record and foreign relations and led to the easing of trade and other economic sanctions, although the country's treatment of its ethnic minorities, particularly in connection with the Rohingya conflict, continued to be condemned by international organizations and many nations.
Following the 2020 Myanmar general election, in which Aung San Suu Kyi's party won a clear majority in both houses, the Burmese military (Tatmadaw) again seized power in a coup d'état. The coup, which was widely condemned by the international community, led to continuous ongoing widespread protests in Myanmar and has been marked by violent political repression by the military. The military also arrested Aung San Suu Kyi and charged her with crimes ranging from corruption to the violation of COVID-19 protocols, all of which have been labeled as "politically motivated" by independent observers, in order to remove her from public life.
Myanmar is a member of the East Asia Summit, Non-Aligned Movement, ASEAN, and BIMSTEC, but it is not a member of the Commonwealth of Nations despite once being part of the British Empire. The country is very rich in natural resources, such as jade, gems, oil, natural gas, teak and other minerals, as well as also endowed with renewable energy, having the highest solar power potential compared to other countries of the Great Mekong Subregion. However, Myanmar has long suffered from instability, factional violence, corruption, poor infrastructure, as well as a long history of colonial exploitation with little regard to human development. In 2013, its GDP (nominal) stood at US$56.7 billion and its GDP (PPP) at US$221.5 billion. The income gap in Myanmar is among the widest in the world, as a large proportion of the economy is controlled by cronies of the military junta. , according to the Human Development Index, Myanmar ranks 147 out of 189 countries in terms of human development. Since 2021, more than 600,000 people were displaced across Myanmar due to the surge in violence post-coup, with more than 3 million people in dire need of humanitarian assistance.
The name of the country has been a matter of dispute and disagreement, particularly in the early 21st century, focusing mainly on the political legitimacy of those using Myanmar versus Burma. Both names derive from the earlier Burmese Mranma or Mramma, an ethnonym for the majority Burman ethnic group, of uncertain etymology. The terms are also popularly thought to derive from Brahma Desha or (Sanskrit) after Brahma.
In 1989, the military government officially changed the English translations of many names dating back to Burma's colonial period or earlier, including that of the country itself: Burma became Myanmar. The renaming remains a contested issue. Many political and ethnic opposition groups and countries continue to use Burma because they do not recognise the legitimacy of the ruling military government or its authority to rename the country.
In April 2016, soon after taking office, Aung San Suu Kyi commented on the question of which name should be used and said that "it is up to you because there is nothing in the constitution of our country that says that you must use any term in particular". She continued, "I use Burma very often because I am used to using it. But it does not mean that I require other people to do that as well. And I'll make an effort to say Myanmar from time to time so you all feel comfortable."
The country's official full name is "Republic of the Union of Myanmar" (ပြည်ထောင်စုသမ္မတ မြန်မာနိုင်ငံတော်). Countries that do not officially recognise that name use the long form "Union of Burma" instead. In English, the country is popularly known as either Burma or Myanmar. In Burmese, the pronunciation depends on the register used and is either ' or '. The name Burma has been in use in English since the 18th century.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| MMK | Myanmar kyat | Ks | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| MY | Burmese language |