Seattle–Tacoma International Airport (Seattle-Tacoma International Airport)
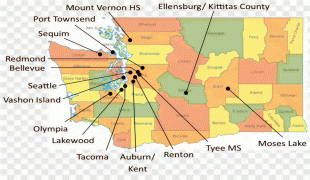
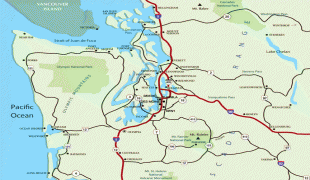
Seattle–Tacoma International Airport, branded as SEA Airport and also referred to as Sea–Tac , is the primary commercial airport serving the Seattle metropolitan area in the U.S. state of Washington. It is in the city of SeaTac, which was named after the airport’s nickname “Sea-Tac”, approximately 14 mi south of Downtown Seattle and 18 mi north-northeast of Downtown Tacoma. The airport, which is the busiest in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, is situated between Portland, Oregon and Vancouver, British Columbia, and is owned by Port of Seattle.
The entire airport covers an area of 2,500 acres, much smaller than other U.S. airports with similar annual passenger numbers. The airport has flights to cities throughout North America, Oceania, Europe, the Middle East, and Asia. It is the primary hub for Alaska Airlines, whose headquarters are near the airport. It is also a hub and international gateway for Delta Air Lines, which has expanded at the airport since 2011. , 31 airlines operate at SEA, serving 91 domestic and 28 international destinations.
The airport was built by the Port of Seattle in 1944 after the U.S. military took control of Boeing Field in World War II. The Port received $1 million from the Civil Aeronautics Administration to build the airport and $100,000 from the City of Tacoma. The first scheduled airline flights were Northwest and Trans-Canada in 1947; Western and United moved from Boeing Field in the next couple of years, and Pan Am moved in 1952–53, but West Coast and successors Air West and Hughes Airwest stayed at Boeing Field until 1971. The original terminal was designed by architect Herman A. Moldenhour. The official opening ceremony took place on July 9, 1947, in front of a crowd of 30,000.
In June 1951 four runways were at 45-degree angles, between 5000 and 6100 ft long; the northeast–southwest and northwest–southeast runways intersected just west of the north–south runway that eventually became today's runway 34R. Runway 34 was lengthened to 7500 ft in 1951, to 8500 ft by 1958, and to 11900 ft by 1962. The extension required the construction of an automobile tunnel for South 188th Street, which opened in July 1961. Runway 34L replaced runway 2 around 1970.
The April 1957 OAG shows 216 departures a week on United, 80 Northwest, 35 Western, 21 Trans-Canada, 20 Pan Am, 20 Pacific Northern and 10 Alaska. The first jet flights were Pan Am Boeing 707s to Honolulu via Portland (OR) in late 1959 (Pan Am's timetable for September 27 shows a weekly jet). In 1966 Scandinavian Airlines began the airport's first non-stop flight to mainland Europe (Pan Am nonstops to London began around 1961). The first concourse opened in July 1959.
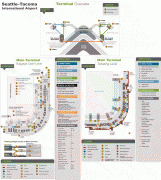
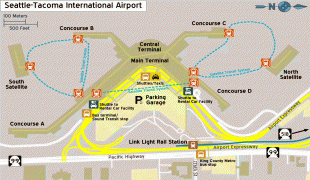
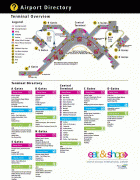
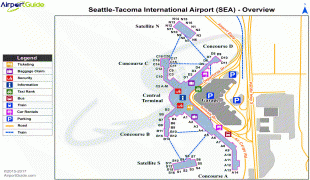
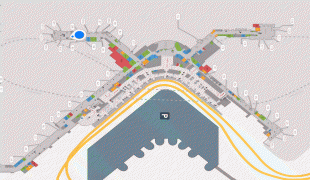
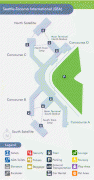
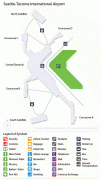
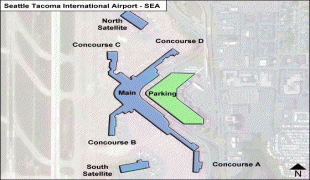
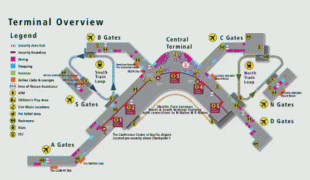
The two-story North Concourse (later dubbed Concourse D) added four gate positions and a new wing 600 ft long and 30 ft wide. The one-story South Concourse (now Concourse A) opened in 1961, adding another 688 ft to the length of the airport. The 800 ft long Concourse B opened in December 1964. It added eight gate positions, bringing the total to 19, a 12000 sqft area housing international arrivals and the offices of U.S. Customs, Immigration, Public Health and the Department of Agriculture. Concourse C opened in July 1966. Just four years later, it was extended to include another 10 gates, bringing the total to 35. The Port embarked on a major expansion plan, designed by The Richardson Associates and lasting from 1967 to 1973, adding a second runway, a parking garage, two satellite terminals and other improvements. In 1973, $28-million new terminal was built over and around the 1949 structure; the new terminal quadrupled the area for public use. On July 1, 1973, the Airport opened two new satellite terminals, along with an underground train system to connect them to the Main Terminal. These fully automatic shuttle trains were the first of their kind in the United States. Also unprecedented in any U.S. airport: as part of the expansion the Port commissioned $300,000 worth of artworks; these were the start of what would become a large public art collection owned by the Port. In the mid-1980s, the Main Terminal was renovated and another 150 ft was added to the north end. Concourse D was expanded in 1987 with a rotunda that added four new gates. In 1993, Concourses B, C, and D were renovated. The project, designed by NBBJ, included the addition of 150000 sqft and the renovation of 170000 sqft of space in Concourses B, C, and D. On June 15, 2004, the 2102 ft new Concourse A was unveiled with 14 new gates, a dozen new restaurants, new artwork and the airport's first moving sidewalks.
Residents of the surrounding area filed lawsuits against the Port in the early 1970s, complaining of noise, vibration, smoke, and other problems. The Port and the government of King County adopted the Sea–Tac Communities Plan in 1976 to address problems and guide future development. The Port spent more than $100 million over the next decade to buy homes and school buildings in the vicinity, and soundproof others nearby. In the mid-1980s, the airport participated in the airport noise-compatibility program initiated by Congress in 1979. Airport-noise contours were developed, real estate was purchased and some homes were retrofitted to achieve noise mitigation.
In 1978 the U.S. ended airline regulation, and the U.S. airlines were allowed to determine routes and fares without government approval. Deregulation resulted in some new service to Seattle, including from TWA, then the fourth-largest U.S. airline, as well as Delta, National, and American.
After the death of U.S. Senator Henry Martin "Scoop" Jackson in 1983, the Seattle Port Commission voted to change the airport's name to the Henry M. Jackson International Airport. Citizens of Tacoma interpreted the change as an insult to their community—the second time in the airport's history that the port authorities had attempted to remove "Tacoma" from the name. The $100,000 Tacoma had provided for the airport's construction during World War II had come with an explicit promise that the city would be included in the airport's name. An additional complicating factor was the existence of another Jackson International Airport (now Jackson–Medgar Wiley Evers International Airport) in Jackson, Mississippi, whose management threatened legal action to preserve its exclusive use of the name. The controversy was resolved after polls of Seattle and Tacoma area residents showed their preference for the original name by margins as much as 5:1. Helen Jackson, the widow of the late Senator Henry M. Jackson, expressed her desire that their family remain neutral in the debate. With a 3–2 vote of the Port of Seattle Commission, the name reverted to Seattle–Tacoma International Airport in early 1984.
In the late 1980s the Port of Seattle and a council representing local county governments considered the future of air traffic in the region and predicted that the airport could reach capacity by 2000. In 1992, the planning committee concluded that the best solution was to add a third runway to the airport and construct a supplemental two-runway airport in one of the neighboring counties. Members of the community opposed a third runway, as did the Highline School District and the cities of Des Moines, Burien, Federal Way, Tukwila, and Normandy Park, but a 1994 study concluded there were no feasible sites for an additional airport. The Port of Seattle approved a plan for the new runway in 1996, prompting a lawsuit from opponents. The Port secured the necessary permits by agreeing to noise reduction programs and environmental protections. Runway opponents appealed these permits, but dropped their challenges in 2004.
The entire airport covers an area of 2,500 acres, much smaller than other U.S. airports with similar annual passenger numbers. The airport has flights to cities throughout North America, Oceania, Europe, the Middle East, and Asia. It is the primary hub for Alaska Airlines, whose headquarters are near the airport. It is also a hub and international gateway for Delta Air Lines, which has expanded at the airport since 2011. , 31 airlines operate at SEA, serving 91 domestic and 28 international destinations.
The airport was built by the Port of Seattle in 1944 after the U.S. military took control of Boeing Field in World War II. The Port received $1 million from the Civil Aeronautics Administration to build the airport and $100,000 from the City of Tacoma. The first scheduled airline flights were Northwest and Trans-Canada in 1947; Western and United moved from Boeing Field in the next couple of years, and Pan Am moved in 1952–53, but West Coast and successors Air West and Hughes Airwest stayed at Boeing Field until 1971. The original terminal was designed by architect Herman A. Moldenhour. The official opening ceremony took place on July 9, 1947, in front of a crowd of 30,000.
In June 1951 four runways were at 45-degree angles, between 5000 and 6100 ft long; the northeast–southwest and northwest–southeast runways intersected just west of the north–south runway that eventually became today's runway 34R. Runway 34 was lengthened to 7500 ft in 1951, to 8500 ft by 1958, and to 11900 ft by 1962. The extension required the construction of an automobile tunnel for South 188th Street, which opened in July 1961. Runway 34L replaced runway 2 around 1970.
The April 1957 OAG shows 216 departures a week on United, 80 Northwest, 35 Western, 21 Trans-Canada, 20 Pan Am, 20 Pacific Northern and 10 Alaska. The first jet flights were Pan Am Boeing 707s to Honolulu via Portland (OR) in late 1959 (Pan Am's timetable for September 27 shows a weekly jet). In 1966 Scandinavian Airlines began the airport's first non-stop flight to mainland Europe (Pan Am nonstops to London began around 1961). The first concourse opened in July 1959.
The two-story North Concourse (later dubbed Concourse D) added four gate positions and a new wing 600 ft long and 30 ft wide. The one-story South Concourse (now Concourse A) opened in 1961, adding another 688 ft to the length of the airport. The 800 ft long Concourse B opened in December 1964. It added eight gate positions, bringing the total to 19, a 12000 sqft area housing international arrivals and the offices of U.S. Customs, Immigration, Public Health and the Department of Agriculture. Concourse C opened in July 1966. Just four years later, it was extended to include another 10 gates, bringing the total to 35. The Port embarked on a major expansion plan, designed by The Richardson Associates and lasting from 1967 to 1973, adding a second runway, a parking garage, two satellite terminals and other improvements. In 1973, $28-million new terminal was built over and around the 1949 structure; the new terminal quadrupled the area for public use. On July 1, 1973, the Airport opened two new satellite terminals, along with an underground train system to connect them to the Main Terminal. These fully automatic shuttle trains were the first of their kind in the United States. Also unprecedented in any U.S. airport: as part of the expansion the Port commissioned $300,000 worth of artworks; these were the start of what would become a large public art collection owned by the Port. In the mid-1980s, the Main Terminal was renovated and another 150 ft was added to the north end. Concourse D was expanded in 1987 with a rotunda that added four new gates. In 1993, Concourses B, C, and D were renovated. The project, designed by NBBJ, included the addition of 150000 sqft and the renovation of 170000 sqft of space in Concourses B, C, and D. On June 15, 2004, the 2102 ft new Concourse A was unveiled with 14 new gates, a dozen new restaurants, new artwork and the airport's first moving sidewalks.
Residents of the surrounding area filed lawsuits against the Port in the early 1970s, complaining of noise, vibration, smoke, and other problems. The Port and the government of King County adopted the Sea–Tac Communities Plan in 1976 to address problems and guide future development. The Port spent more than $100 million over the next decade to buy homes and school buildings in the vicinity, and soundproof others nearby. In the mid-1980s, the airport participated in the airport noise-compatibility program initiated by Congress in 1979. Airport-noise contours were developed, real estate was purchased and some homes were retrofitted to achieve noise mitigation.
In 1978 the U.S. ended airline regulation, and the U.S. airlines were allowed to determine routes and fares without government approval. Deregulation resulted in some new service to Seattle, including from TWA, then the fourth-largest U.S. airline, as well as Delta, National, and American.
After the death of U.S. Senator Henry Martin "Scoop" Jackson in 1983, the Seattle Port Commission voted to change the airport's name to the Henry M. Jackson International Airport. Citizens of Tacoma interpreted the change as an insult to their community—the second time in the airport's history that the port authorities had attempted to remove "Tacoma" from the name. The $100,000 Tacoma had provided for the airport's construction during World War II had come with an explicit promise that the city would be included in the airport's name. An additional complicating factor was the existence of another Jackson International Airport (now Jackson–Medgar Wiley Evers International Airport) in Jackson, Mississippi, whose management threatened legal action to preserve its exclusive use of the name. The controversy was resolved after polls of Seattle and Tacoma area residents showed their preference for the original name by margins as much as 5:1. Helen Jackson, the widow of the late Senator Henry M. Jackson, expressed her desire that their family remain neutral in the debate. With a 3–2 vote of the Port of Seattle Commission, the name reverted to Seattle–Tacoma International Airport in early 1984.
In the late 1980s the Port of Seattle and a council representing local county governments considered the future of air traffic in the region and predicted that the airport could reach capacity by 2000. In 1992, the planning committee concluded that the best solution was to add a third runway to the airport and construct a supplemental two-runway airport in one of the neighboring counties. Members of the community opposed a third runway, as did the Highline School District and the cities of Des Moines, Burien, Federal Way, Tukwila, and Normandy Park, but a 1994 study concluded there were no feasible sites for an additional airport. The Port of Seattle approved a plan for the new runway in 1996, prompting a lawsuit from opponents. The Port secured the necessary permits by agreeing to noise reduction programs and environmental protections. Runway opponents appealed these permits, but dropped their challenges in 2004.
| IATA Code | SEA | ICAO Code | KSEA | FAA Code | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Telephone | +1 (206) 787 5388 | Fax | |||
| Home page | Hyperlink |
Map - Seattle–Tacoma International Airport (Seattle-Tacoma International Airport)
Map
Country - United_States
 |
 |
| Flag of the United States | |
Indigenous peoples have inhabited the Americas for thousands of years. Beginning in 1607, British colonization led to the establishment of the Thirteen Colonies in what is now the Eastern United States. They quarreled with the British Crown over taxation and political representation, leading to the American Revolution and proceeding Revolutionary War. The United States declared independence on July 4, 1776, becoming the first nation-state founded on Enlightenment principles of unalienable natural rights, consent of the governed, and liberal democracy. The country began expanding across North America, spanning the continent by 1848. Sectional division surrounding slavery in the Southern United States led to the secession of the Confederate States of America, which fought the remaining states of the Union during the American Civil War (1861–1865). With the Union's victory and preservation, slavery was abolished nationally by the Thirteenth Amendment.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| USD | United States dollar | $ | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| EN | English language |
| FR | French language |
| ES | Spanish language |