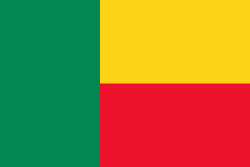
Flag of Benin
The national flag of Benin (drapeau du Bénin) is a flag consisting of two horizontal yellow and red bands on the fly side and a green vertical band at the hoist. Adopted in 1959 to replace the French Tricolour, it was the flag of the Republic of Dahomey until 1975, when the People's Republic of Benin was established. The new regime renamed the country and changed the flag to a green field with a red star in the canton. This version was utilized until multi-party democracy was re-established in 1990, coinciding with the Revolutions of 1989. The new government promptly restored the original pre-1975 flag.
Under French colonial rule over Dahomey, French authorities forbade the colony from having its own regional flag. This was because they were worried that this could increase nationalistic sentiment and lead to calls for independence. However, with the rise of the decolonization movement in Africa, the French were obliged to grant limited autonomy to Dahomey as a self-governing republic within the French Community. This was granted on December 4, 1958, and a search for a national flag began soon after.
The new flag was chosen on November 16, 1959, and remained unchanged when Dahomey became independent less than a year later on August 1, 1960. In 1972, a coup d'état took place in the country, with the new government aligning itself with Marxist–Leninist ideals. In order to symbolize the revolutionary change, the country was renamed Benin and a new flag was instituted three years later. It featured a green field charged with a five-pointed red star in the top-left canton. The new flag was never adopted by law, however, making it only the de facto flag of Benin.
The green flag remained in place until 1990, when economic problems and the weakening of the Soviet Union's power due to the Revolutions of 1989 culminated in the collapse of the People's Republic of Benin. The original flag from 1959 was reinstated on August 1, 1990.
Under French colonial rule over Dahomey, French authorities forbade the colony from having its own regional flag. This was because they were worried that this could increase nationalistic sentiment and lead to calls for independence. However, with the rise of the decolonization movement in Africa, the French were obliged to grant limited autonomy to Dahomey as a self-governing republic within the French Community. This was granted on December 4, 1958, and a search for a national flag began soon after.
The new flag was chosen on November 16, 1959, and remained unchanged when Dahomey became independent less than a year later on August 1, 1960. In 1972, a coup d'état took place in the country, with the new government aligning itself with Marxist–Leninist ideals. In order to symbolize the revolutionary change, the country was renamed Benin and a new flag was instituted three years later. It featured a green field charged with a five-pointed red star in the top-left canton. The new flag was never adopted by law, however, making it only the de facto flag of Benin.
The green flag remained in place until 1990, when economic problems and the weakening of the Soviet Union's power due to the Revolutions of 1989 culminated in the collapse of the People's Republic of Benin. The original flag from 1959 was reinstated on August 1, 1990.
National flag
Country - Benin
Warning: getimagesize(/Image/Map/MP2395170.gif): failed to open stream: No such file or directory in /home/mapnlee7/public_html/MAPNALL/article.php on line 532
 |
 |
From the 17th to the 19th century, political entities in the area included the Kingdom of Dahomey, the city-state of Porto-Novo, and other states to the north. This region was referred to as the Slave Coast from the early 17th century due to the high number of people who were sold and trafficked during the Atlantic slave trade to the New World. France took over the territory in 1894, incorporating it into French West Africa as French Dahomey. In 1960, Dahomey gained full independence from France. As a sovereign state, Benin has had democratic governments, military coups, and military governments. A self-described Marxist–Leninist state called the People's Republic of Benin existed between 1975 and 1990. In 1991, it was replaced by the multi-party Republic of Benin.
